Barley
Barley, one of the most common cereal grains in the world and a member of the grass family, is widely cultivated around the world in regions with moderate weather. Tonnes of barley are exported from India to a number of other nations. India has been exporting more barley every year as a result of the rising global demand for the grain. Good quality barley and barley products are exported by Indian barley exporters. Various types of barley are exported from India.
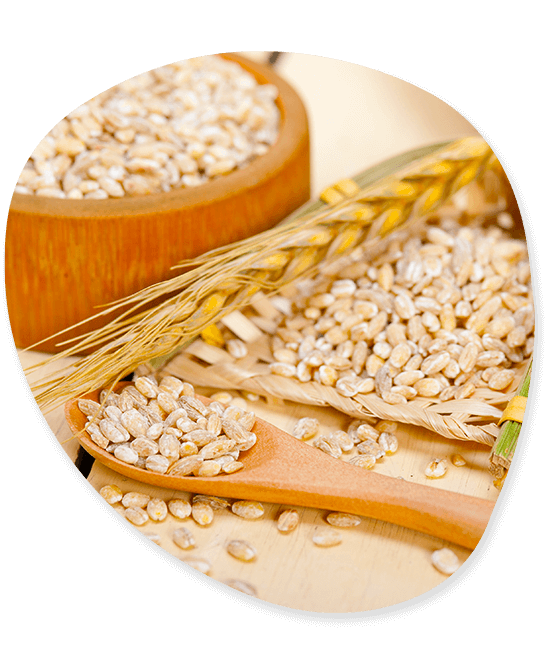

Nutrients:
- Calories – 354 calories
- Dietary Fiber – 17 g
- Total Carbohydrate 73 g
Vitamins:
- Vitamin B1
Minerals:
- Molubdenum
- Manganese
- Selenium
- Copper
- Chromium
- Phosphorous
- Magnesium
- Niacin
Pre-Shipment Inspection:
Standard Packing:
- We provide packaging in terms of 5, 10, 20, 25, 50 and 100kg also, as per the customers’ (country) requirement.
BARLEY VARIETIES WE EXPORT
India is home to a large number of barley cultivars. Most of these types of barley, including Azad, Ratna, Vijaya, and others, are imported from India. Most of these types are exported to other countries by the Indian exporter of barley. The main kinds of barley exported from India are.
AZAD (K.125)
In general, eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal are good places to grow the Azad variety. According to reports, this particular barley type is somewhat resistant to the yellow rust disease. K.125 works well as grain and fodder. The Azad variety usually takes 115–120 days to reach maturity. Under irrigated conditions, it has a yield potential of 35–38 quintals of grain per hectare.

RATNA
Eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal rainfed regions received the Ratna type of barley. According to reports, this type can withstand both salty and alkaline soil conditions very well. The ratna plant is supposed to reach maturity in 125–130 days and produce a respectable yield even in poor environmental circumstances. This variety’s plants have strong tillering capacity.
VIJAYA
For the rainfed areas of western Uttar Pradesh, I Delhi, and Madhya Pradesh, the Vijaya variety has been released. The maturation period is 120–125 days. In comparison to other barley types, the Vijaya variety’s plants are shorter in height. This cultivar has a 30-35 quintal grain output potential per hectare.

RS-6
Developed in Rajasthan, the RS-6 variety of Barley is suitable for cultivation under both rainfed as well as irrigated conditions. This variety has generally been recommended for central and eastern Rajasthan. It matures in about 130-135 days and has a yield potential of 35 to 40 quintals of grain per hectare.
RANJIT (DL- 70)
A six-row, heavily tillering barley variety called Ranjit or DL-70 is suggested for commercial cultivation solely in Punjab. This cultivar can thrive in irrigation-friendly environments. It has a 30-35 quintal grain output potential per hectare.
C- L64
The tall, six-row barley variety C-164 has compact ears and lengthy awns. This grain typically has a vivid, amber colour. Yellow rust is believed to be resistant to C-14. Because of its stiff straw, it is more suited for growth in irrigated environments. This cultivar produces approximately 30-32 quintals of grain per hectare.

LSB-2
Six-row naked type barley is known as the LSB variety. It is a cultivar that can thrive in higher elevations, such as the hills of Himachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. This variety, which matures in 145–150 days, has a 25–30 quintal grain output potential per hectare.
