Green Gram
The green gramme, commonly referred to as mung bean, is essentially a member of the legume family of plant species. Tonnes of green gramme are shipped out of India each year by the green gramme exporter. Globally, green gramme is becoming more and more well-liked. This could be the cause of the sharp increase in green gramme exports coming out of India. A fantastic moment to enter the global market is now for Indian exporters of green gramme. The export of several types of green gramme is included in the export of green gramme.
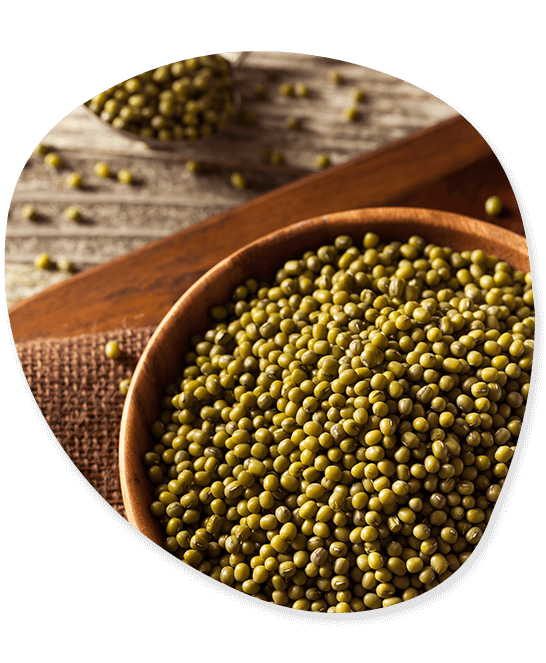

Nutrients:
- Calories – 347 calories
- Total Carbohydrate 63 g
- Dietary fiber 16 g
Vitamins:
Minerals:
Protein:
Pre-Shipment Inspection:
Standard Packing:
GREEN GRAM VARIETIES WE EXPORT
Numerous types of green grammes, including CO 1, ADT 1, JGG 1, and other variations, are imported from India. The Indian exporter of mung beans exports high-quality goods while taking health and safety standards into consideration. The main Green Gram cultivars that are exported are listed below.
CO 1
CO 1 is a Green Gram cultivar that was first introduced from India in 1952. It is a locally sourced pure-line product. 135 days are necessary for maturation. The yield of grains is about 750 kg/ha. This type can be nourished by rain.

ADT 1
The ADT is a green gramme cultivar that was introduced in 1966. It is purely a local Aduthurai line selection. This particular strain of green gramme matures in about 80 days. This variety produces about 500 kg/ha of grain when grown with rainwater. This type works well on fallow rice.
JGG 1 (RAJENDRAN)
This green gramme variety was introduced in 1972 and is a Jayankondam native. the green gramme cultivar JGG 1. This cultivar needs about 65 days to reach maturity. JGG 1 has a grain yield of about 625 kg/ha. According to reports, this cultivar can withstand drought.

KM 1
The KM 1 variety of green gramme is one that India exports to various nations across the world. It became available in 1978. It is claimed that S.8 and PS 16 were crossed to create it. This variety requires 65 to 70 days to reach maturity. This cultivar produces about 708 kg/ha of grain.
KM 2
A green gramme cultivar introduced in 1978 is called the KM 2. The yield of this type of green gramme under rainfed conditions is 767 kg/ha. This particular strain of green gramme is a pod borer and YMV-tolerant.
PAIYUR1
The Paiyur1 type of green gramme was introduced in 1988 and is a pure line selection from DPT 703. About 85 to 90 days are needed for this particular kind of green gramme to reach maturity. This cultivar produces about 700kg/ha of grain. This type is ideally suited for rainfed tracts in the Dharmapuri, Madurai, Ramnad, Tirunelveli, and Periyar Districts and has a low incidence of YMV.

VAMBAN 1
The hybrid offshoot of the green gramme variety Vamban 1 is (S.8 x PIMS 3). In 1989, this variety was made available. This cultivar takes roughly 65 to 70 days to reach maturity. Vamban 1 has a grain yield of about 800 kg/ha. It is rumoured to be YMV-tolerant.
VBN (GG) 2
This cultivar is a hybrid of MH 309 and VGG 4. It was made public in 2001. This particular strain of green gramme reaches maturity in 65 to 70 days. This variety’s 750kg/ha grain output when grown with rainwater. The leaves are lobed and resistant to YMV, while the grains are glossy.
