Groundnut
In essence, groundnut is a member of the family of legumes. It was most likely first domesticated and grown in the Paraguayan valleys. Tonnes of groundnuts are exported from India to a number of international destinations. The rising global demand for the product is likely to blame for India’s groundnut exports over the years. In the 2018–19 fiscal year, the Indian exporter of groundnuts sent around 4,89,187.13 MT of groundnuts. Consequently, it can be claimed that the export of groundnuts is a booming industry.
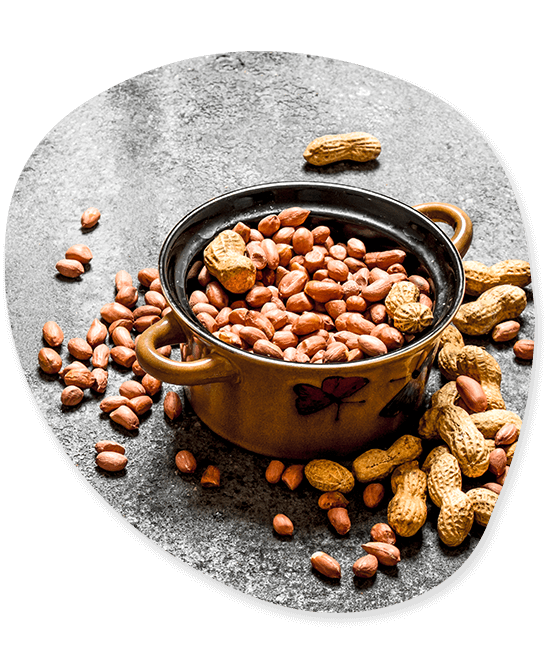

Nutrients:
Minerals:
Vitamins:
Protein:
Pre-Shipment Inspection:
Standard Packing:
- We provide packaging in terms of 5, 10, 20, 25, 50 and 100kg also, as per the customers’ (country) requirement.
GROUNDNUT VARIETIES WE EXPORT
Numerous groundnut types, including TLG 45, Narayani, Vasundhara, and many others, are imported from India. The best groundnuts in the world are sent by an Indian company to several nations. The following are the main varieties of groundnut exported.
TLG 45
At the releasing facility at MAU, Latur, the TLG 45 variety was introduced in 2007. This variety has a yield potential of approximately 1506 kg/ha. This seed has about 51% oil content. Maharashtra is the suggested state for this type. It is a cultivar with big seeds.

NARAYANI (TCGS 29)
The Narayani variety was launched in 2007 at the ANGRAU, Tirupati, releasing centre. This variety has a potential yield of about 3764 kg/ha. This cultivar has about 48% oil content. It can withstand moisture stress throughout the middle of the season.
VASUNDHARA (DH 101)
Groundnuts of the Vasundhara type were introduced in 2007. This cultivar has a yield potential of roughly 2877 kg/ha. The cultivar has about 50% oil content. It has been suggested that West Bengal, Orissa, Jharkhand, and Assam grow it. This type is resistant to PBND and stem rot.

VL- MOONGPHALI-1
The VL- Moongphali-1 variety of groundnuts was introduced in 2008 at the VPKAS, Almora, releasing centre. This cultivar has a yield potential of roughly 1943kg/ha. This cultivar, which is resistant to late leaf spot and root rot, has been suggested for cultivation in Uttarakhand.
UTKARSH (CSMG 9510)
The oil content of this cultivar, which was introduced in 2009 at CSAUAT, Mainpuri, is about 49%. It has been suggested that this type be grown in Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and Northern Rajasthan. It has a fresh seed dormancy of up to 40–45 days and is rust-resistant. It is advised for use throughout the Kharif season.
JAWAHAR GROUNDNUT 23 (JGN 23)
2009 saw the publication of The Jawahar Groundnut 23 in JNKVV, Khargone. This variety has a yield potential of approximately 1631 kg/ha. This cultivar has about 49% oil content. This type can withstand LLS and ELS. It has been suggested for the Kharif season and is also drought resistant.

GREESHMA
This Greeshma cultivar, which was introduced in 2009 at ANGRAU, Tirupati, has a production potential of approximately 2000–2500 kg/ha. This cultivar has about 49% oil content. It has been suggested that Andhra Pradesh plant this cultivar. It is resistant to aflatoxin, drought, extreme temperatures, and LLS.
KADIRI 8
At ANGRAU, Kadiri, the Kadiri 8 variety of groundnut was introduced in 2009. The estimated yield potential is 1523 kg/ha. This seed has about 47% oil content. This type is resistant to sucking pests and leaf spots, and is advised for cultivation in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
MALLIKA
The Mallika variety of groundnuts was introduced in 2009 at RAU, Hanumangarh, and has a 2579 kg/ha production potential. About 48% of this variety’s weight is oil. This type has bold seeds and is resistant to PBND and collar rot. It is advised for use throughout the Kharif season.
One of the top importers of groundnuts from India is Vachhani Impex. For our customers, Vachhani Impex offers hassle-free food export services. Groundnut exporting can occasionally be a challenging task. But don’t worry! To ensure that your products arrive at their destination safely and in good condition, our experts at Vachhani will assist you at every stage. Contact Vachhani right away if you’re seeking for groundnut export!
