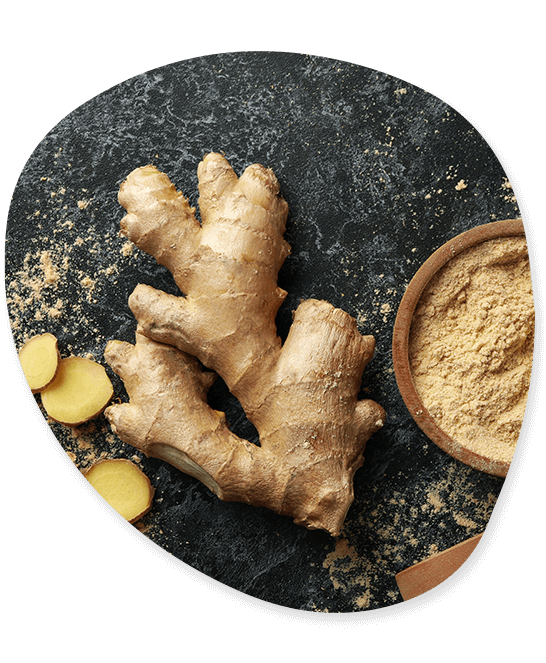
Ginger
One of the first known eastern spices is thought to be ginger. It is widely utilised in Indian cuisine as well as other cuisines throughout the world. The Indo-Malaysian region is home to many members of the tropical Ginger family. India has been exporting ginger at a high rate for a few years. India’s export of ginger is subject to strict health and quality standards. Ginger exports are becoming a reliable source of income for exporters.

Pre-Shipment Inspection:
Standard Packing:
GINGER VARIETIES WE EXPORT
India is one of the world’s top producers of ginger, producing about 385.33 thousand tonnes annually. India exported 35,616.35 tonnes of ginger in 2011–12, up from 8,332.91 tonnes in 2007–08. As a result, India’s ginger exporter has raised the quality of its goods and is now exporting more ginger each year.
RIO-DE-JANEIRO
Rio-de-Janeiro is one of the popular varieties of ginger. This variety can be recognised by a few traits. Rhizome size is substantial, and the skin is buff in colour. Rio de Janeiro is less fibrous, has a strong flavour, and is very pungent.

THINGPUI
One of the ginger cultivars grown in India is called Thingpui. This ginger cultivar has a strong flavour. The Thingpui’s rhizome is described as being medium in size. A buff-colored skin tone can be recognised. Thingpui contains a lot of flavour and is less fibrous.
WYNAD
One of the earliest known eastern spices is a type of ginger called wynad. The Wynad rhizome is bold in size. Like many other types of ginger, the skin is buff in colour. It is less fibrous and more pungent.

MARAN
Maran is a strong-flavored and pungent kind of ginger. The Maran’s rhizome is described as being modest in size. The skin of a Maran is buff in colour. Additionally, this ginger species is less fibrous.
NADIA
Ginger that is yellowish in colour is called nadia. For the Nadia kind of ginger, the rhizome is described as being medium to bold in size. Nadia has a mild flavour and a medium level of odour. Additionally, it is less fibrous than other ginger cultivars.
IISR-REJATHA
This ginger cultivar was introduced in 2001 and has a bumpy, rounded appearance. It is believed to have rhizomes that are bold and form three-layered, dense clusters. This particular type is high in oil and oleoresin but poor in fibre.

IISR-MAHIMA
The IISR-Mahima, which was introduced in 2001, is chubby. Kerala is one of the regions where this type of ginger is popular. This type of ginger contains strong, fibrous rhizomes. The IISR-Mahima has root-knot nematode resistance.
IISR-VARADA
IISE-Varada is a high producing and high-quality ginger variety. It has medium-sized reddish-brown scales and plump rhizomes. Farmers claim that the Varada cultivar has a low fibre content and is disease-tolerant.
India is not only the world’s top producer of ginger; it is also the top exporter of ginger. The regions of the North East, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim account for more than half of all ginger output in India. Vachhani Impex is one of the top exporters of ginger from India if you’re interested in doing so. They ensure that your products are delivered safely around the world thanks to their vast knowledge and skill in this industry.
